What is Incognito Mode?
Incognito Mode (also known as Privacy Mode or Private Window) is a browsing mode offered by most browsers. When you surf the web using it, your browsing history, search records, cookies, and other site data won't be saved by the browser.

How Incognito Mode Works
When you browse the web using Incognito Mode, the browser won't save the following information:
Browser history: For instance, if you visited a shopping site and looked at a hat, once you close the incognito window, the shopping site won't appear in your browser history when you check it later.
Search records: If you typed "iPhone 15 Pro Max" into the search bar, this search record won't be saved by the browser once the incognito window is closed.
Cookies: If you logged into Facebook, the browser won't save your login information once the incognito window is closed. The next time you visit Facebook, you'll need to re-enter your username and password.
Form data: If you were registering an account on a website and filled out the registration information, after entering your name and email address and closing the incognito window, this information won't be saved by the browser. You won't find this information pre-filled on other website forms.
Browser cache: If you watched a video on a video site, to improve playback speed and efficiency, the browser might temporarily store part or all of the video file on your computer. This is what's known as browser cache. Even if your internet connection is interrupted, the video can still play for a while. However, once the incognito window is closed, these temporarily stored video files will be automatically deleted and won't take up your disk space.
While it seems like the browser in Incognito Mode won't save certain information, the truth is, Incognito Mode can't fully protect your personal privacy. Next, we'll tell you the secret behind this.
Incognito Mode Can't Prevent Tracking
We've written many articles about browser fingerprinting before, where websites can usually obtain user device information through various techniques.
Incognito Mode Can Not Prevent Tracking!
We can do a simple test to prove this. Using both a normal window and an incognito window in Chrome, visit a fingerprint detection website at the same time to see if Incognito Mode can prevent the site from obtaining device information.
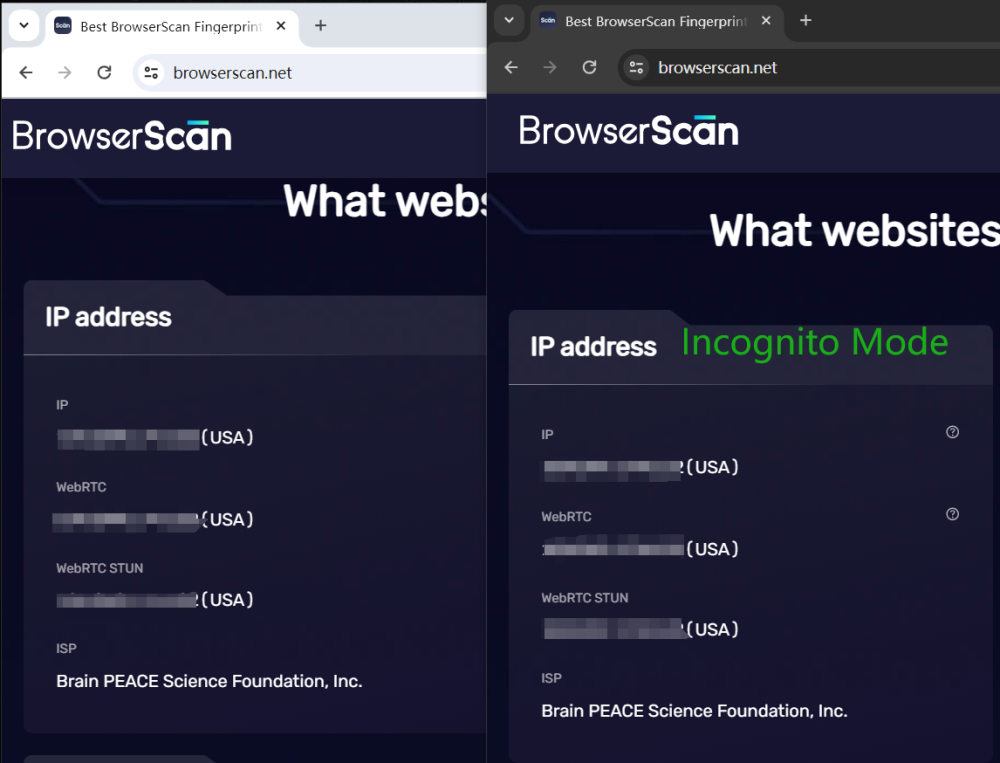
IP Address/Geolocation
Whenever we visit a website, we need to provide our IP address. But if you're not using a VPN or proxy server, even in Incognito Mode, the site can still get your real IP address through WebRTC. In other words, even with Incognito Mode, you might still leak your real IP address.
We've written article before explaining how websites can map users' real geolocation through some IP databases. Some IP databases can even accurately locate geolocation information down to the street level.
Local Time
Just when you're relieved that using a VPN or proxy server can hide your IP address, websites have already used "time" to judge your browsing behavior.
Websites can compare the time based on IP and local time to determine whether a user is using a VPN or proxy server. If some websites have strict restrictions on users accessing via VPN, you might be restricted from accessing the site due to "inconsistent times".
As you can see, Incognito Mode can't change your local time, which is something that most people may overlook.
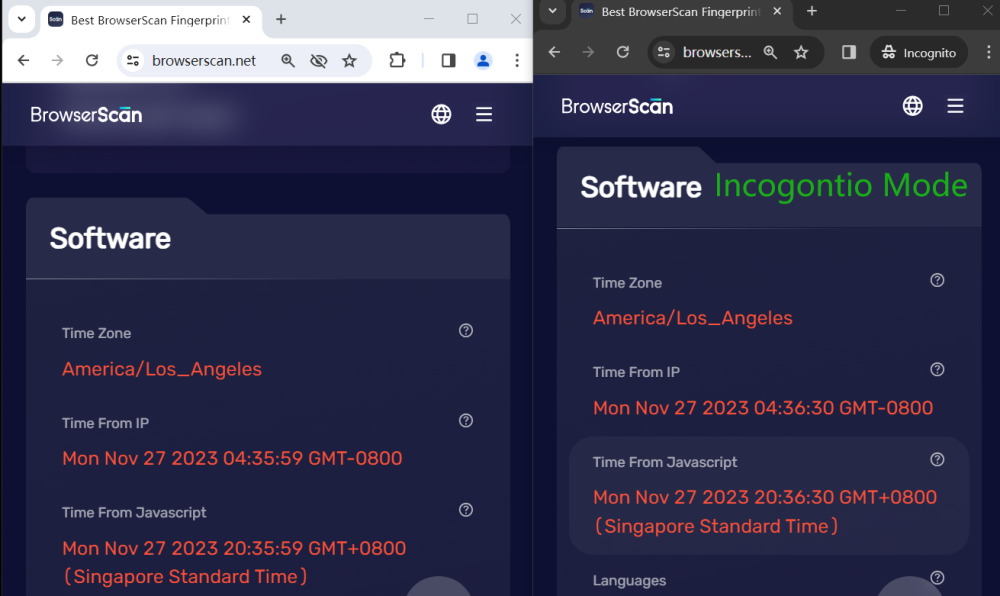
Local IP is in Singapore, proxy server IP is in the United States, the two times and time zones are not the same.
Browser Fingerprints
A browser fingerprint is a nearly unique identifier generated by websites by collecting user device and browser information, just like a person's fingerprints. This information includes browser type, version, operating system, screen resolution, Canvas fingerprint, WebGL fingerprint, etc.
Let's look at the fingerprint detection results of the two windows to see if Incognito Mode can prevent websites from collecting these fingerprints.
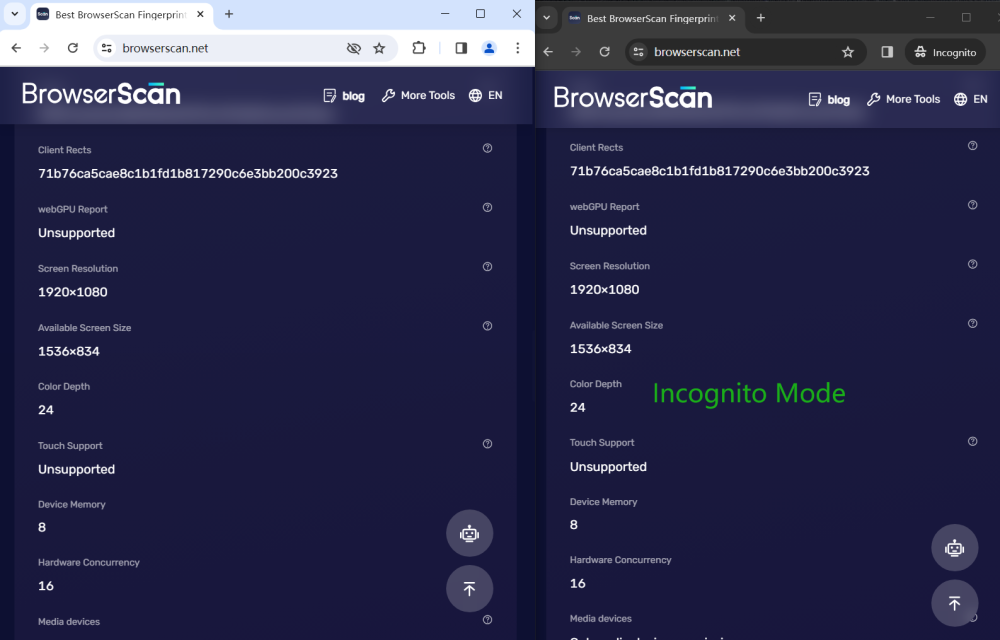
Hardware
Compare the values in the image carefully, the values in the normal window and the incognito window are the same, there is no change. The website still "recognizes" your device.
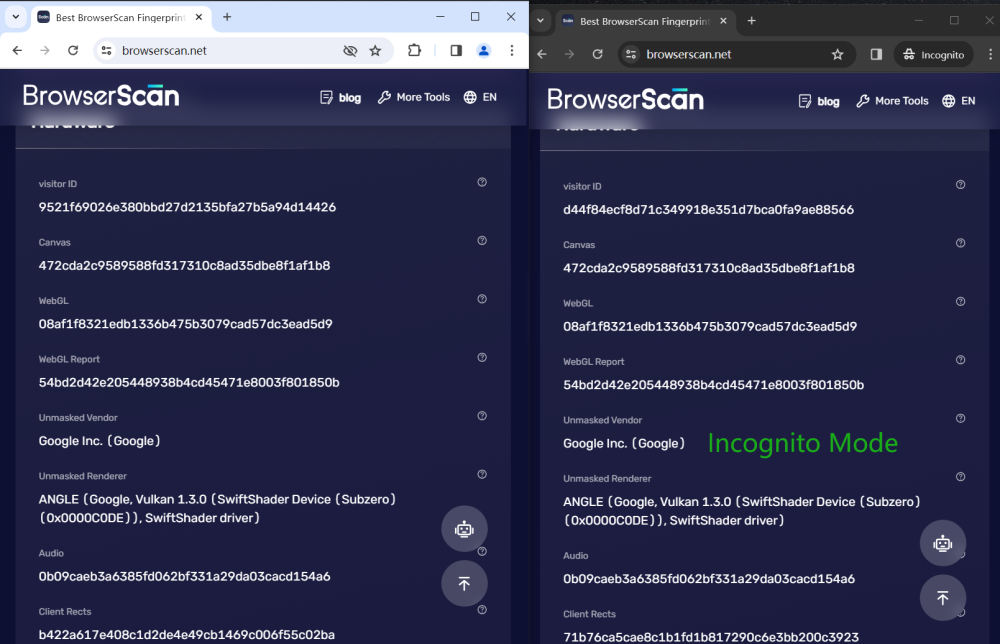
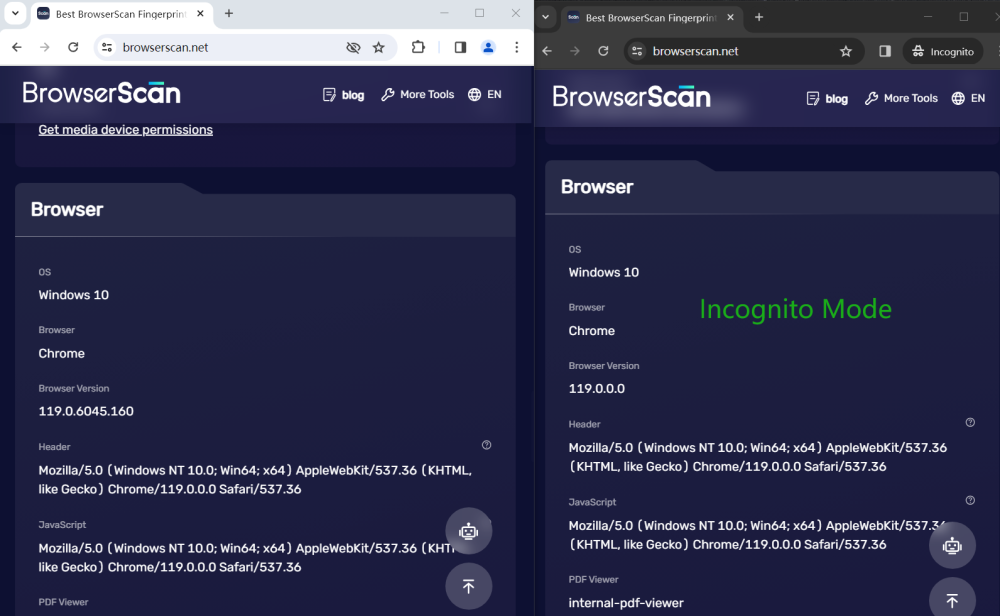
Software Information
Both windows display the same browser version, operating system, and other information. Incognito Mode also cannot change UserAgent.
Conclusion
From the above detection results, we can prove that: the browser's incognito mode cannot prevent websites from obtaining device information. Websites can still identify and track users through the uniqueness of browser fingerprints. Even if the user changes the IP address, the website can still accurately identify the user.
If you just want to visit certain websites without letting the website record your login status, and you don't want the browser to retain history records that reflect your personal preferences, then using Incognito Mode is undoubtedly the most convenient.
But if you want to fully protect your personal privacy and don't want to leave your real "traces" on the Internet, then using an anti detect browser is your best solution.
