What is an IP address?
IP address
An IP address, full name Internet Protocol Address, is used to identify each device on the Internet, much like every household has a unique street address. Every device connected to the Internet needs to have an IP address.
IPv4 vs IPv6
IP addresses are divided into IPv4 addresses and IPv6 addresses.
IPv4, short for Internet Protocol version 4, is one of the most widely used protocols on the Internet.
An IPv4 address consists of 32-bit binary numbers, i.e., four groups of numbers ranging from 0 to 255. For example, 192.168.1.1, 134.110.68.72, 46.108.92.133... IPv4 can represent a total of 4,294,967,296 addresses, approximately 4.2 billion addresses.

Now, with over 7 billion people globally, the number of devices connected to the Internet has far exceeded 7 billion. The quantity of IPv4 addresses is no longer sufficient to assign one IP address to each device. In order to address the depletion of IPv4 addresses, IPv6 addresses were created.
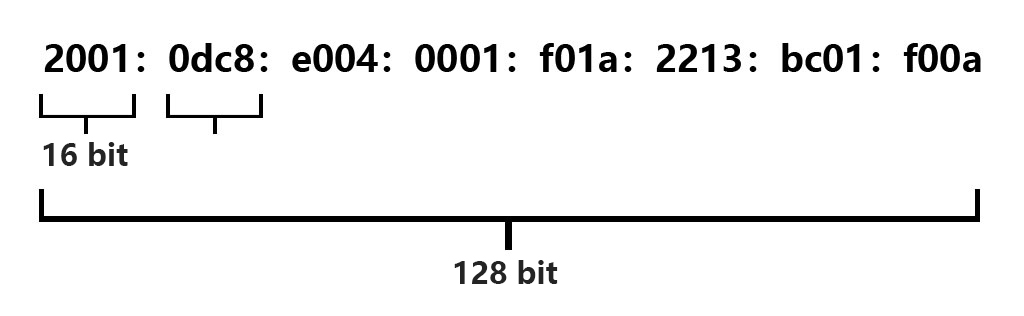
IPv6 consist of 8 groups, with each group composed of 4 numbers or letters from 0 to 9, A to F.
IPv6 are 128 bits long, capable of representing 2 to the power of 128 addresses: 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456.
If you're interested, you can patiently count the units in this string of numbers. If you still can't grasp the scale, let me provide a vivid analogy: We could allocate an IPv6 address for every single grain of sand on Earth.
Since IPv6 addresses require support from Internet Service Provider(ISP) equipment, we seldom come across them in our daily usage. If you encounter an IPv6 address for the first time, don't be alarmed and think your IP address has turned into gibberish. It simply means your ISP has assigned you an IPv6 address. You can still use Internet as usual.
Geolocation, Time Zone, Local Time
IP addresses, much like phone numbers, have different ranges for various countries and regions. Therefore, some organizations and companies maintain extensive databases of IP addresses and their corresponding geolocations. These databases, also known as IP geolocation databases, contain a wealth of information about the geolocations associated with IP addresses. By using these databases, you can inquire about the geolocation of an IP address.
Geolocation
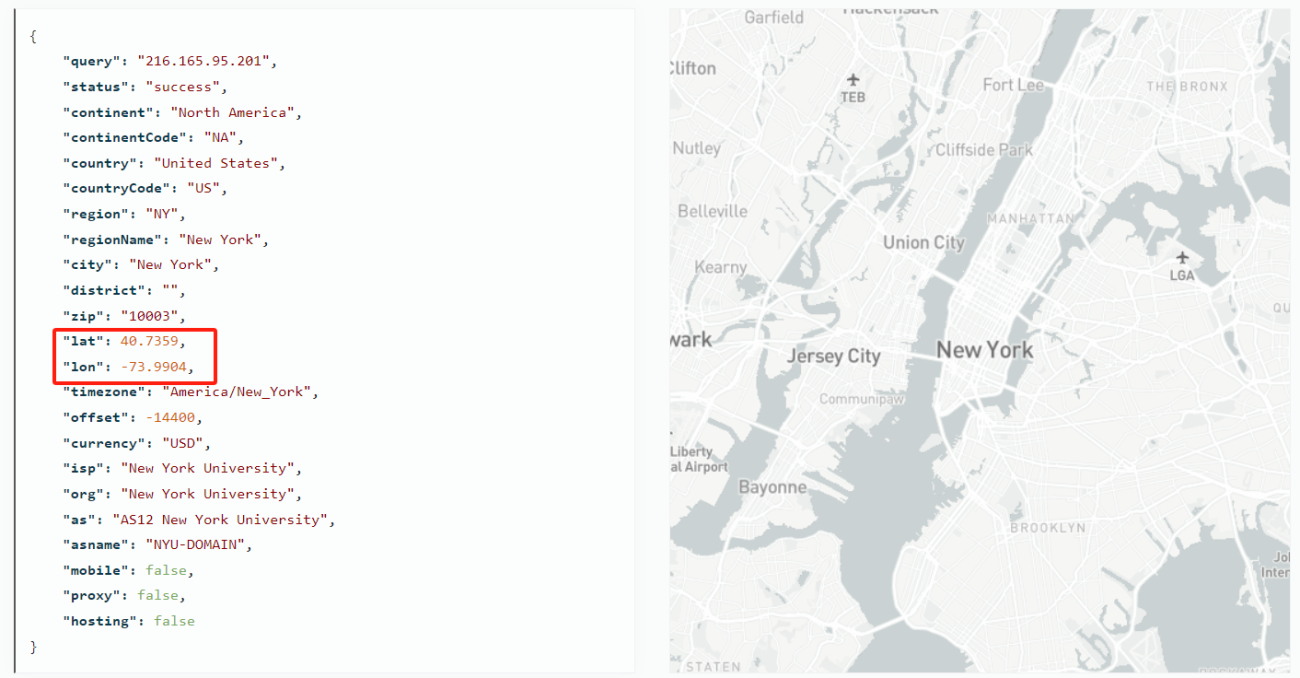
Using BrowserScan's IP lookup tool, you can determine the country/region to which an IP address belongs. For example, the IP address 216.165.95.201 is located in New York City, USA. On BrowserScan, you can view the information provided by various IP databases to compare different results.
Furthermore, with the help of other tools, you can ascertain the approximate geographic coordinates of an IP address - its latitude and longitude.
lat: Latitude, range: [-90,90] (indicating the north-south position)
lon: Longitude, range: [-180,180] (indicating the east-west position)
Time Zone and Local Time
Once the country/region of an IP address is determined, a website can determine the time zone and local time of that IP. For example, when you visit BrowserScan, under the "Software" section, you can see the analysis of your IP address by the website.

Summary
In conclusion, through an IP address, websites can determine the country/region, city, approximate geographic coordinates, time zone, and local time. To some extent, an IP address can also be considered a type of browser fingerprint. Websites use the IP address in conjunction with other browser fingerprints to more accurately identify and track users.
Read Also
Browser Fingerprinting Guide for Beginners
10 Browser Fingerprints to Know in 5 Minutes
