Did you know? Each time you surf the web, your browser might be quietly leaking your information. It's not just one or two types, but over 20 kinds. This information could include your geographical location, your operating system, your browser version, and even whether your device is a desktop or a mobile device.
So, what exactly is the information that's being leaked? And how can you protect yourself from it? The upcoming content from BrowserScan will reveal all these details for you.
Time/Location
IP Address
The IP address is a unique identifier for each device on the internet, which can be used to find a user's approximate geographical location. Every time you visit a website, your device sends a request to the website's server, which includes your IP address.
Moreover, when you engage in video or voice chat on a webpage, devices establish a direct connection through WebRTC technology. WebRTC might expose your real IP address, even if you are using a VPN or proxy.
Through your IP address, websites can know your approximate geographical location (country, city, latitude, and longitude), and even your internet service provider. Without proper protection measures, malicious attackers might exploit your IP address for cyber attacks, or track your online behavior through your IP address.

DNS Information
DNS information refers to how your device resolves website domain names into IP addresses.
Websites can obtain this information through WebRTC or the timing-allow-origin HTTP response header. This can help websites optimize content distribution and improve loading speeds. However, DNS information can also be used to track your online behavior or infer your network environment.
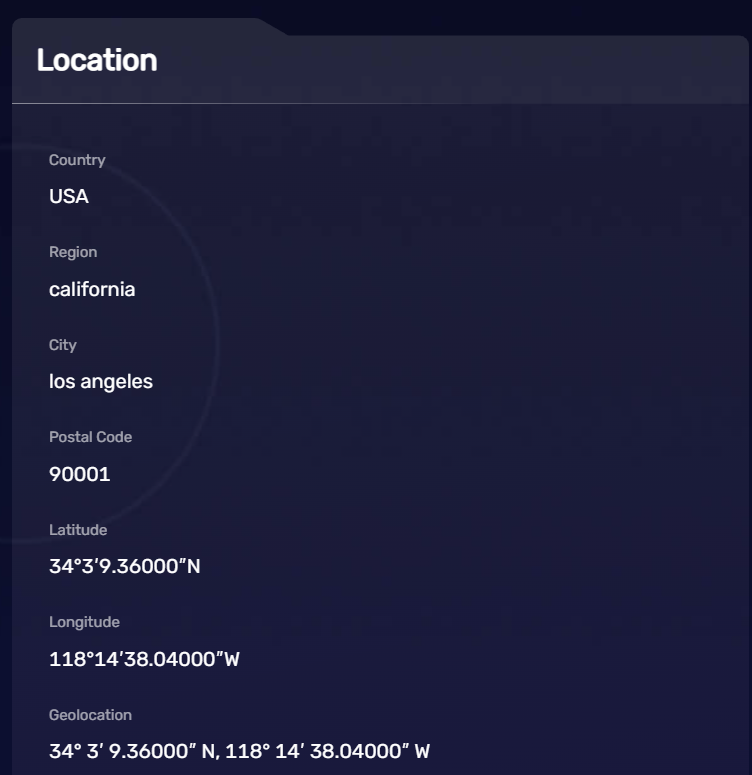
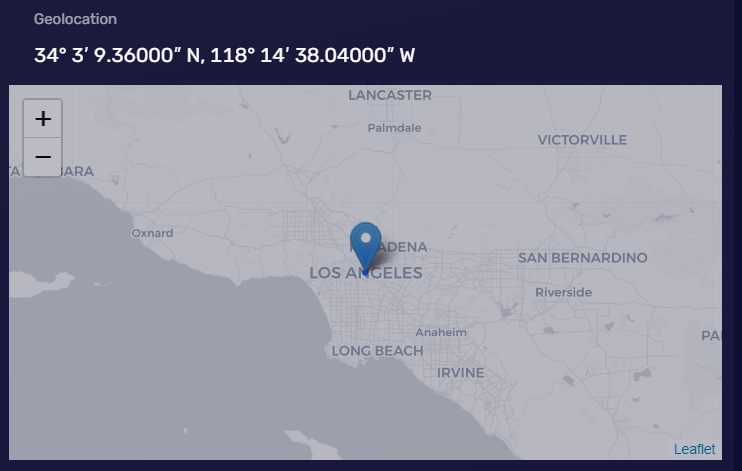
Geolocation
Geolocation refers to the physical location information of your device. Websites can obtain this through the navigator.geolocation object, but it requires your explicit permission.
This can help websites provide location-based services, such as maps, weather forecasts, etc. However, geographical location information can also be used to track your behavior and infringe on your privacy. Without proper protective measures, malicious websites might attempt to obtain your geographical location information.
System Time
System time refers to the current date and time of your device. Websites can obtain this information through the JavaScript Date object. This can help websites provide time-based services, such as displaying your local time.
However, if your system time does not match the time of the location of your IP address, it might reveal that you are using a VPN or proxy.

Local Time/Time Zone
Websites can query the geographical location information corresponding to the IP address, thereby inferring the user's time zone. Then, combined with UTC time, the user's local time can be calculated. The accuracy of this method depends on the accuracy of the IP address and the accuracy of the mapping from IP to geographical location.

Software Info
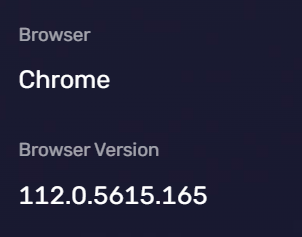
Browser Type and Version
The browser type and version information can tell a website which browser you are using (such as Chrome, Firefox, etc.) and the version number of the browser.
This information is usually included in the User-Agent field of each HTTP request. Websites can use this information to provide content suitable for your browser or prompt you to update your browser. However, it can also be used to identify and track users, or exploit vulnerabilities in specific browsers for attacks.
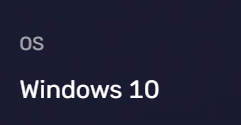
Operating System
Operating system information can tell a website which operating system your device is running (such as Windows, MacOS, Linux, Android, etc.). This information is usually also included in the User-Agent field.
Websites can use this information to provide services suitable for your operating system or prompt you to update your operating system. Similarly, it can also be used to identify and track users, or to exploit vulnerabilities in specific operating systems for attacks.
Cookie
Cookies are small data files that are stored on your device and are used to save your personal settings, login information, etc.
Whenever you visit a website, the browser sends the website's cookies to the server. This allows the website to remember your information and provide personalized services. However, cookies can also be used to track your online behavior, and in malicious websites, they can be used to steal your personal information.
Language Settings
Language settings refer to the preferred language of your browser. Websites can obtain this information through the Accept-Language field in the HTTP request header or the navigator.language property. This can help websites provide content that adapts to your language preferences.

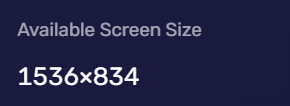
Browser Window Size
The browser window size refers to the width and height of your browser window.
Websites can obtain this information through window.innerWidth and window.innerHeight. This can help websites provide a page layout that adapts to the size of your browser window.
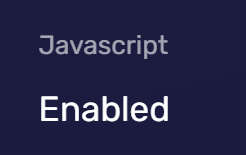
JavaScript Enabled
JavaScript is a commonly used web scripting language, and if it's disabled, many features of a webpage will not work.
Websites can detect whether JavaScript is enabled by attempting to execute JavaScript code. This can help websites decide whether they need to provide alternative content without JavaScript. However, if JavaScript is disabled, it may expose your concern for privacy protection, making you a potential target for specific attacks.
Cookies Enabled
Cookies are a way for websites to store information on your device, and if they're disabled, many features of a website will not function properly.
Websites can detect whether cookies are enabled by attempting to read and write cookies. This can help websites decide whether they need to provide an alternative solution without cookies.

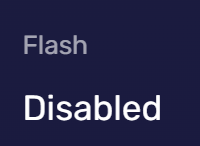
Flash Enabled
Flash is a commonly used web plugin for playing animations, videos, etc. If Flash is disabled or does not exist, websites can detect this by trying to use Flash's JavaScript code.
This can help websites decide whether they need to provide alternative content without Flash. However, Flash has many known security issues, and if Flash is enabled, you may face more security risks.
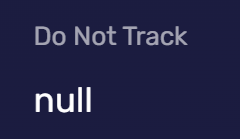
Do Not Track Enabled
Do Not Track is a browser setting used to tell websites that you do not wish to be tracked. Websites can obtain this setting through the navigator.doNotTrack property. Websites that respect this setting will not track your online behavior. Unfortunately, the Do Not Track setting is not mandatory, and many websites choose to ignore it. Moreover, the Do Not Track setting itself can also be used to generate your device fingerprint.
Local and Session Storage
Local storage and session storage are two ways to store data in the browser, which can store more data than cookies and are more flexible. Websites can obtain data from these storages through window.localStorage and window.sessionStorage. This can help websites save user data and provide persistent personalized settings. However, without proper protection measures, malicious websites may try to read sensitive data from these storages.
Hardware Info
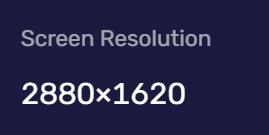
Screen Resolution
Screen resolution refers to the pixel width and height of your device's screen. This can help websites provide page layouts and images that fit your device's screen. However, screen resolution can also be used to generate your device fingerprint.
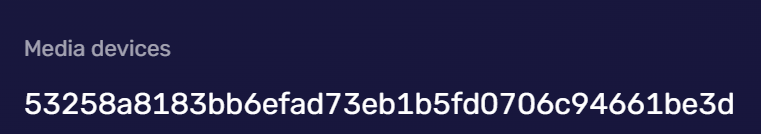
Media Device Information
Websites can obtain user's media device information, but explicit permission from the user is required. The information obtained includes the type of device (audio input device, audio output device, video input device, etc.), the device's ID, the device's label (provided the user has already granted access to the device), etc.
To protect user privacy, browsers may impose certain restrictions on this information. For example, the values of the deviceId and label properties will be hidden unless the user has already granted access to the media device.
Fonts and Color Depth
Fonts are the types of fonts available on your device, and color depth is the number of bits of color your screen can display.
Websites can obtain this information through Flash or JavaScript's Canvas API. This can help websites provide a better user experience, such as using fonts supported by the user's device, or displaying appropriate images based on the color depth.


Hardware
This information includes the number of processor cores on your device, the model of your graphics card, etc. Websites can obtain this information through navigator.hardwareConcurrency or the WebGL DEBUG_RENDERER_INFO extension.
This can help websites provide content that suits your hardware performance, such as allocating tasks based on the number of processor cores, or choosing appropriate graphics rendering methods based on the model of the graphics card. However, hardware information can also be used to generate your device fingerprint, used to track your online behavior. In some cases, hardware information may be used to discover vulnerabilities in your device for targeted attacks.


Battery Status
Battery status includes the battery level and charging status of your device.
Websites can obtain this information through the navigator.getBattery() method. This can help websites provide services that adapt to your device's battery status, such as reducing resource consumption when the battery is low.
Touch Support
Touch support refers to whether your device supports touch screen operation. Websites can detect this through methods like "ontouchstart" in window. This can help websites provide interaction methods that suit your device, such as touch sliding.

Behavioral Information
Mouse Movement and Click Behavior
Mouse movement and click behavior refer to your mouse operations while browsing the web. Websites can obtain this information by listening to events like mousemove and mousedown.
This can help websites provide interaction methods based on user behavior, such as displaying tips, dynamically adjusting layouts, etc. However, mouse movement and click behavior can also be used to generate your behavioral fingerprint, used to track your online behavior.
Keyboard Input Behavior
Keyboard input behavior refers to your keyboard operations while browsing the web. Websites can obtain this information by listening to events like keydown and keypress.
This can help websites provide interaction methods based on user behavior, such as autocomplete, hotkeys, etc. However, keyboard input behavior can also be used to generate your behavioral fingerprint, used to track your online behavior.
Conclusion
With the advancement of technology, websites can obtain more and more information from users. The more information they get, the more accurate the user profile they can create. While you are immersed in the personalized content provided by the website, your personal information may also be leaked.
If you have multiple e-commerce accounts and social accounts at this time, obtaining this information will undoubtedly affect your business. Therefore, to prevent browsers from leaking more information, take the following measures to protect the privacy and security of the account:
Use the latest version of the browser: The latest version of the browser usually includes the latest security updates and privacy protection features.
Browse in privacy mode: Most browsers offer a privacy mode or incognito mode. In this mode, the browser will not save your browsing history, search records, cookies, etc.
Disable or restrict cookies: You can disable cookies in your browser settings, or only allow websites you trust to set cookies.
Use VPN or proxy: This can hide your real IP address, but it should be noted that some websites may obtain your real IP address through technologies like WebRTC.
Use anti-tracking plugins: Some browser plugins, such as Privacy Badger and uBlock Origin, can prevent websites from tracking your online behavior.
Pay attention to authorization: When a website requests access to your location information, camera, microphone, etc., you should carefully consider whether to give authorization.
Regularly clear browser cache: This can clear information that may be used to track your online behavior.
Use HTTPS: Try to only visit websites that use HTTPS. HTTPS can protect your communication content from being eavesdropped on.
Be careful with sharing personal information: Try not to share your personal information on websites, such as your address, phone number, etc.
Use anti-detect browsers: Proxy server + anti-detect browser, the best solution for multi-account owners. But don't forget to use BrowserScan to check whether the browser fingerprint is real and whether the real IP address is leaked.
